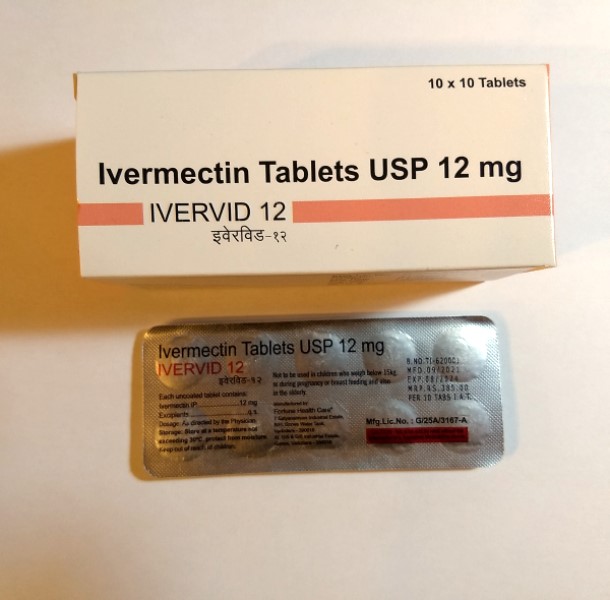
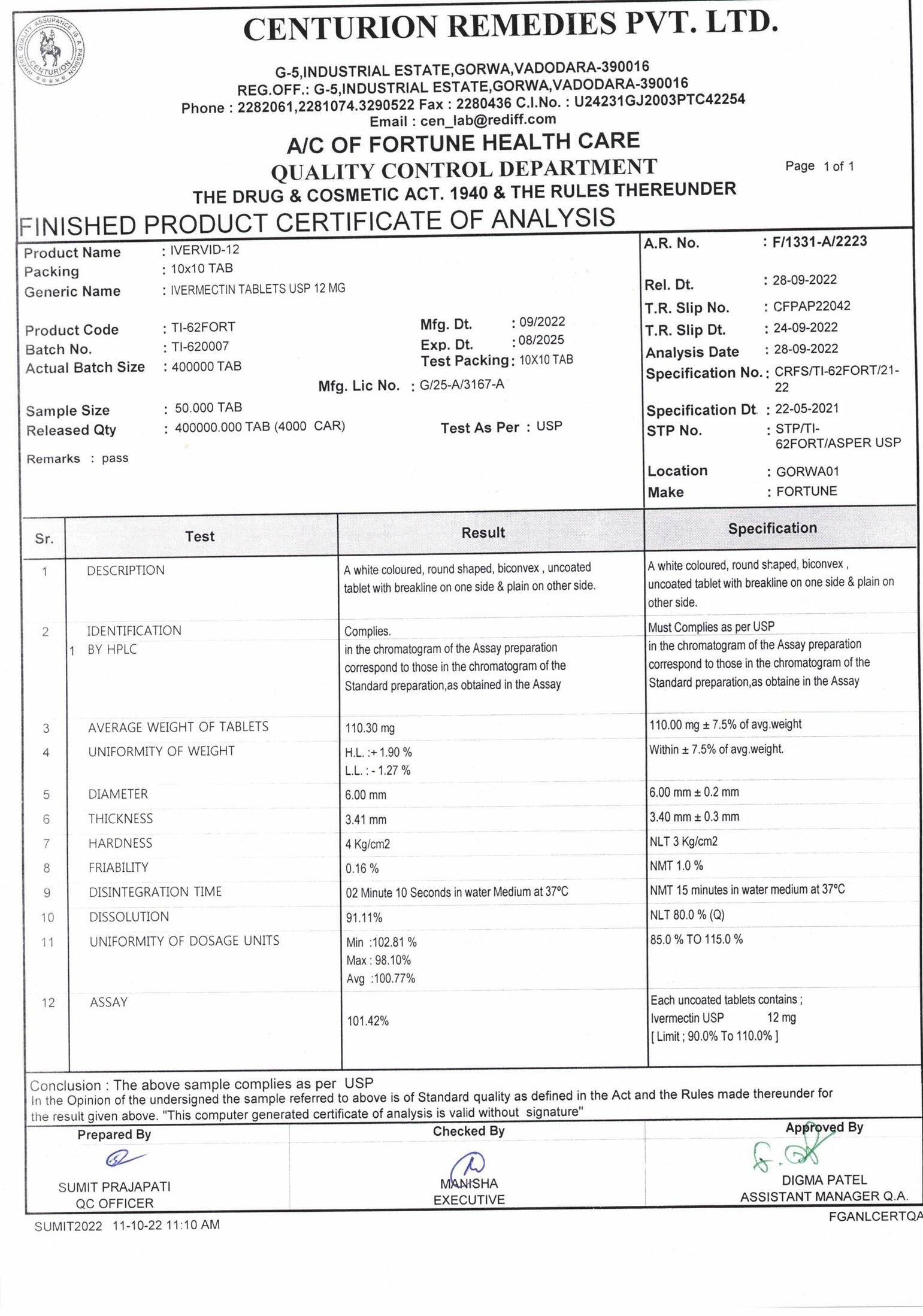
IVERVID 12 MG (IVERMECTIN)
$130.00 – $2,820.00
| Active Ingredient | Ivermectin |
|---|---|
| Indication: | Scabies, Filariasis |
| Manufacturer: | FORTUNE |
| Strength: | 12 Mg |
| Packaging: | 10 tablets in 1 strip |
| Delivery Time: | 22 Working days |
Ivermectin is a medication primarily used to treat certain parasitic infections, such as river blindness and strongyloidiasis, as well as some skin conditions caused by parasites. It is not commonly prescribed for other purposes. Here are some rare and lesser-known facts about ivermectin:
- Discovery and development: Ivermectin was discovered in the 1970s by researchers at the Kitasato Institute in Japan, and it was initially developed as a veterinary anthelmintic (deworming) drug. It was later found to be effective in treating human parasitic infections and was approved for human use in the 1980s.
- Nobel Prize recognition: The discovery and development of ivermectin led to the awarding of the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2015 to Dr. Satoshi Ōmura and Dr. William C. Campbell. This highlights the significant impact that ivermectin has had on global public health efforts.
- Mass drug administration programs: Ivermectin is one of the few drugs recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) for mass drug administration (MDA) programs aimed at controlling and eliminating certain neglected tropical diseases. These programs have helped reduce the global burden of these diseases and improve the quality of life for millions of people.
- Potential use for COVID-19: Some studies have suggested that ivermectin may have antiviral properties against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. However, current evidence is insufficient to support its widespread use for the prevention or treatment of COVID-19, and more research is needed to determine its potential role in managing this pandemic.
- Environmental concerns: While ivermectin is generally well-tolerated in humans, its widespread use in veterinary and human medicine has raised concerns about the potential impact on the environment, particularly aquatic ecosystems. Studies have shown that ivermectin residues in soil and water can harm some non-target organisms, such as certain insects and fish. Therefore, it is crucial to use ivermectin responsibly and in accordance with local guidelines and recommendations.
In conclusion, while ivermectin is primarily known for its effectiveness in treating certain parasitic infections, these rare facts highlight its broader impact on global public health, its recognition through the Nobel Prize, and the ongoing research into its potential applications.
INFORMATION:
Ivermectin is a medication primarily used to treat certain parasitic infections, such as river blindness and strongyloidiasis, as well as some skin conditions caused by parasites. It is not commonly prescribed for other purposes. Here are some rare and lesser-known facts about ivermectin:
- Discovery and development: Ivermectin was discovered in the 1970s by researchers at the Kitasato Institute in Japan, and it was initially developed as a veterinary anthelmintic (deworming) drug. It was later found to be effective in humans and has since been widely used for various parasitic infections.
- Nobel Prize: The discovery of ivermectin and its potential for treating parasitic infections led to the awarding of the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine to Satoshi Ōmura and William C. Campbell.
- Mass drug administration: Ivermectin is part of mass drug administration (MDA) programs in many countries, particularly in Africa, to combat neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), such as onchocerciasis (river blindness) and lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis).
- COVID-19: Some individuals and groups have advocated for the use of ivermectin as a treatment for COVID-19, despite limited and conflicting evidence supporting its effectiveness against the virus.
- Safety profile: Ivermectin is generally considered safe when used as prescribed for its approved indications. However, it can cause side effects, including dizziness, nausea, and low blood pressure. In rare cases, it may cause severe allergic reactions or neurological side effects.
- Contraindications: Ivermectin should not be used in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to the drug or its components. It should also be avoided in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as its safety in these populations has not been established.
- Drug interactions: Ivermectin may interact with certain medications, including some antifungal drugs, anticonvulsants, and immunosuppressive medications. It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you are taking before starting ivermectin.
- Alternative names: Ivermectin is also known by its brand names, such as Stromectol, Soolantra, and Ivomec.
- Veterinary use: Ivermectin is commonly used in veterinary medicine for the treatment and prevention of parasites in animals, including dogs, horses, and livestock.
- Research and development: Ongoing research is exploring the potential use of ivermectin in other medical conditions, such as cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and bacterial infections. However, more research is needed to determine its safety and effectiveness in these areas.
BENEFITS:
Ivermectin has several benefits when used for its intended purposes, such as treating parasitic infections and skin conditions caused by parasites. Here are some of the benefits:
- Effective treatment: Ivermectin is highly effective in treating and controlling certain parasitic infections, including onchocerciasis (river blindness) and strongyloidiasis. It is also used to treat lymphatic filariasis, scabies, and some other skin conditions caused by parasites.
- Low-cost: Ivermectin is an inexpensive drug, making it an affordable option for people in developing countries where parasitic infections are more prevalent.
- Single-dose treatment: In many cases, a single dose of ivermectin is sufficient to treat a parasitic infection, which makes it a convenient and straightforward treatment option.
- Reduced transmission: By effectively treating parasitic infections, ivermectin can help reduce the transmission of these infections to others, thus contributing to public health efforts.
- Safety profile: Ivermectin is generally well-tolerated and has a favorable safety profile. However, it is essential to use the drug as prescribed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as there can be side effects and potential drug interactions.
Although ivermectin has shown promise in some preliminary studies for treating COVID-19, its effectiveness for this purpose is still under investigation and not yet proven. The current consensus among health authorities and medical professionals is that ivermectin should not be used as a treatment for COVID-19 outside of clinical trials.
PRECAUTIONS:
When using ivermectin, it is essential to take certain precautions to ensure its safe and effective use. Here are some precautions to consider:
- Consult a healthcare professional: Always consult a healthcare professional before starting ivermectin, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or are taking any other medications.
- Dosage and frequency: Follow the prescribed dosage and frequency of ivermectin, as using too much or too little of the drug can be ineffective or cause side effects.
- Drug interactions: Inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you are taking, as ivermectin may interact with certain drugs, such as antifungal medications, anticonvulsants, and immunosuppressive medications.
- Allergic reactions: If you have a known allergy to ivermectin or any of its components, do not use the drug. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction, such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, lips, or throat.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Ivermectin should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding, as its safety in these populations has not been established.
- Avoid alcohol: Some studies suggest that alcohol may increase the risk of side effects when using ivermectin. It is best to avoid alcohol while taking the drug.
- Monitor for side effects: Although ivermectin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Be sure to monitor for any adverse reactions and inform your healthcare provider if you experience any side effects.
- Proper storage: Store ivermectin at room temperature, away from heat, moisture, and direct sunlight. Keep the medication out of reach of children and pets.
- Disposal: If you no longer need ivermectin or it has expired, do not flush it down the toilet or pour it down the drain. Instead, dispose of it properly according to local guidelines or return it to a pharmacy for safe disposal.
- Regular check-ups: If you are using ivermectin for an ongoing condition, schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Remember, these precautions are general guidelines, and it is essential to follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider when using ivermectin.
| QUANTITY | 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 700, 1000, 2000, 5000 |
|---|
Related products
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized
Uncategorized